How To Install Apache Maven on Ubuntu
In this tutorial, we show you in detail how to install Apache Maven in Ubuntu Linux.
What is Apache Maven?
Apache Maven has been developed as a tool for management and understanding of software projects.
Apache Maven is based on the concept of the project object model (POM), and thanks to Maven, it is possible to manage the compilation, the reports and the documentation of a project from a central piece of information allowing its total control.
The objectives with which Apache Maven was created are:
- Allow the construction process to be as natural as possible
- Provide a uniform construction system
- Offer project quality information
- Provide guidelines for the development of best practices
- Allow a transparent migration to new functions
Step 1: Install Java
The first step is to install the ‘python-software-properties' package using the following command:
sudo apt install -y python-software-properties
Now we are going to add the Java PPA repository with the following command:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:webupd8team/java
Once this repository is added, we proceed to update the packages on this one:
sudo apt update
Apache Maven requires JDK 1.7 or higher, and in this case, we are going to install JDK 1.8, to do this, we will install Java from the PPA using the apt command as follows:
sudo apt install -y oracle-java8-installer
Once this process is finished we can visualize the Java version by executing the following:
java -version
 Step 2: Download Apache Maven
Step 2: Download Apache Maven
The next step is to download the Apache Maven binary code using the wget command, and we will use the /usr/local/src directory as the Maven home directory.
First, we will go to the indicated directory:
cd /usr/local/src
Then we will download the Apache Maven binaries by running:
sudo wget http://www-us.apache.org/dist/maven/maven-3/3.5.2/binaries/apache-maven-3.5.2-bin.tar.gz
We proceed to extract the downloaded file and delete the compressed file:
sudo tar -xf apache-maven-3.5.2-bin.tar.gz sudo rm -f apache-maven-3.5.2-bin.tar.gz
We can change the name of the directory by executing:
mv apache-maven-3.5.2/ apache-maven/
Step 3: Setup Apache Maven Environment
Now, let's configure the environment for Apache Maven, there we will define some environment variables that Apache Maven needs, such as JAVA_HOME, M2_HOME and the PATH environment for Maven binary files.
To do this, we go to the, etc/profile.dy directory and create a new configuration file called maven.sh:
cd /etc/profile.d/ sudo maven.sh
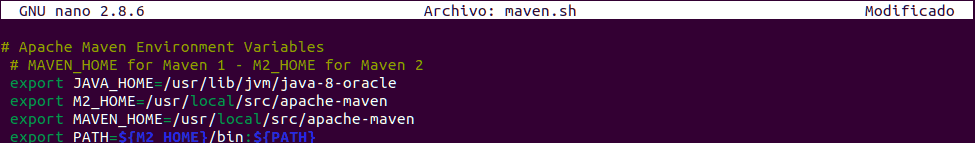
In this new file, we will paste the following:
# Apache Maven Environment Variables
# MAVEN_HOME for Maven 1 - M2_HOME for Maven 2
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-oracle
export M2_HOME=/usr/local/src/apache-maven
export MAVEN_HOME=/usr/local/src/apache-maven
export PATH=${M2_HOME}/bin:${PATH}
Now we are going to make executable the script ‘maven.sh' and then we will apply the configuration executing the command ‘source' like this:
chmod +x maven.sh source maven.sh
Step 4: Validate Apache Maven
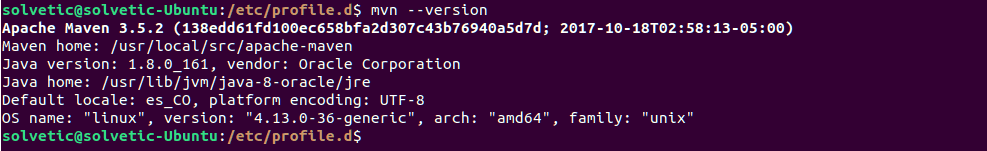
To verify the installation of Apache Maven, we will execute the following:
mvn --version
The installation of Apache Maven 3.2 has been completed, and we can see that it runs under 64-bit Linux (amd64), with Java 1.8 installed, and Maven's home directory is
/usr/local/src/apache-maven.
In this way, we have learned how to install and validate Apache Maven in Ubuntu.


 Step 2: Download Apache Maven
Step 2: Download Apache Maven